Design Patterns
Design patterns are
solutions to software design problems you find again and again in real-world
application development. Patterns are about reusable designs and interactions
of objects.
A design pattern isn't a finished design that can be
transformed directly into code. It is a description or template for how to
solve a problem that can be used in many different situations.
Design
patterns can speed up the development process by providing tested, proven
development paradigms. Effective software design requires considering issues
that may not become visible until later in the implementation. Reusing design
patterns helps to prevent subtle issues that can cause major problems and
improves code readability for coders and architects familiar with the patterns.
The 23 Gang of Four (GoF)
patterns are generally considered the foundation for all other patterns. They
are categorized in three groups:
¨ Creational,
¨ Structural,
and
¨ Behavioral
Creational
Design Patterns
These
design patterns are all about class instantiation. This pattern can be further
divided into class-creation patterns and object-creational patterns. While
class-creation patterns use inheritance effectively in the instantiation
process, object-creation patterns use delegation effectively to get the job
done.
Abstract Factory
|
Creates an
instance of several families of classes
|
Builder
|
Separates
object construction from its representation
|
Factory Method
|
Creates an
instance of several derived classes
|
Prototype
|
A fully
initialized instance to be copied or cloned
|
Singleton
|
A class of
which only a single instance can exist
|
Structural
Patterns
These design
patterns concern class and object composition. Concept of inheritance is used
to compose interfaces and define ways to compose objects to obtain new
functionalities.
Adapter
|
Match
interfaces of different classes
|
Bridge
|
Separates an
object’s interface from its implementation
|
Composite
|
A tree
structure of simple and composite objects
|
Decorator
|
Add
responsibilities to objects dynamically
|
Facade
|
A single class
that represents an entire subsystem
|
Flyweight
|
A fine-grained
instance used for efficient sharing
|
Proxy
|
An object
representing another object
|
Behavioral
Patterns
These
design patterns are specifically concerned with communication between objects. By doing so, these patterns
increase flexibility in carrying out this communication.
Chain
of Resp.
|
A way of
passing a request between a chain of objects
|
Command
|
Encapsulate a
command request as an object
|
Interpreter
|
A way to include
language elements in a program
|
Iterator
|
Sequentially
access the elements of a collection
|
Mediator
|
Defines
simplified communication between classes
|
Memento
|
Capture and
restore an object's internal state
|
Observer
|
A way of
notifying change to a number of classes
|
State
|
Alter an
object's behavior when its state changes
|
Strategy
|
Encapsulates
an algorithm inside a class
|
Template
Method
|
Defer the
exact steps of an algorithm to a subclass
|
Visitor
|
Defines a new
operation to a class without change
|
Architectural
Patterns
An
architectural style, sometimes called an architectural pattern, is a set of
principles—a coarse grained pattern that provides an abstract framework for a family
of systems. An architectural style improves partitioning and promotes design
reuse by providing solutions to frequently recurring problems.
MVC
The Model-View-Controller (MVC)
architectural pattern separates an application into three main components: the
model, the view, and the controller.
¨ Model–view–controller (MVC) is a software architecture
pattern
¨ Originally formulated in the late 1970s by Trygve Reenskaug as part of the Smalltalk
¨ Code reusability and separation of concerns
¨ Originally developed for desktop, then adapted for internet
applications
Model
¨ Set of classes that describes the data we are working with as
well as the business
¨ Rules for how the data can be changed and manipulated
¨ May contain data validation rules
¨ Often encapsulate data stored in a database as well as code
used to manipulate the data
¨ Most likely a Data Access Layer of some kind
¨ Apart from giving the data objects, it doesn't have
significance in the framework
View
¨ Defines
how the application’s user interface (UI) will be displayed
¨ May
support master views (layouts) and sub-views (partial views or controls)
¨ Web:
Template to dynamically generate HTML
Controller
¨ The
core MVC component
¨ Process
the requests with the help of views and models
¨ A
set of classes that handles
¤ Communication
from the user
¤ Overall
application flow
¤ Application-specific
logic
¨ Every
controller has one or more "Actions"
MVC Frameworks
PHP
|
Cake
PHP, Code Igniter
|
Java
|
Spring
|
Perl
|
Catalyst,
Dancer
|
Python
|
Django,
Flask, Grok
|
Ruby
|
Ruby
on Rails, Camping, Nitro, Sinatra
|
Java Script
|
Angular
JS, JavaScript MVC, Spine
|
.NET Framework
|
ASP.NET
MVC
|
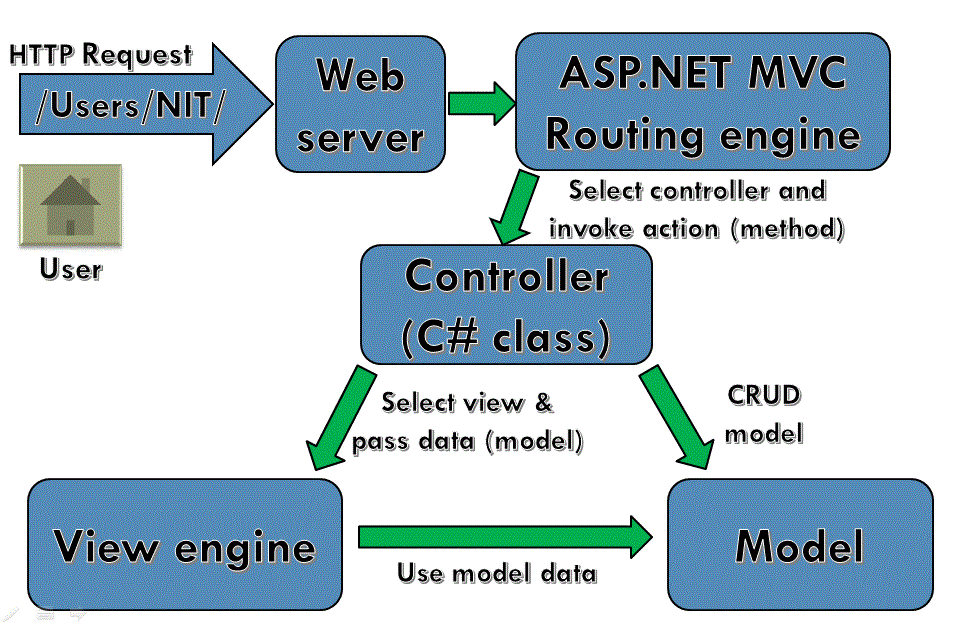
The MVC Pattern for
Web
¨ Incoming
request routed to Controller
¤ For
web: HTTP request
¨ Controller
processes request and creates presentation Model
¤ Controller
also selects appropriate result (view)
¨ Model
is passed to View
¨ View
transforms Model into appropriate output format (HTML)
¨ Response
is rendered (HTTP Response)
Stage
|
Details
|
Receive first request for the application
|
In the Global.asax
file, Route objects are added to the RouteTable object.
|
Perform routing
|
The UrlRoutingModule module uses the first
matching Route object in theRouteTable collection to create
the RouteData object, which it then uses to create
aRequestContext (IHttpContext) object.
|
Create MVC request handler
|
The MvcRouteHandler object
creates an instance of the MvcHandler class and passes it
the RequestContext instance.
|
Create controller
|
The MvcHandler object uses
the RequestContext instance to identify
theIControllerFactory object (typically an instance of the DefaultControllerFactoryclass)
to create the controller instance with.
|
Execute controller
|
The MvcHandler instance
calls the controller s Execute method.
|
Invoke action
|
Most controllers inherit from
the Controller base class. For controllers that do so,
theControllerActionInvoker object that is associated with the controller
determines which action method of the controller class to call, and then
calls that method.
|
Execute result
|
A typical action method might receive user input, prepare
the appropriate response data, and then execute the result by returning a
result type. The built-in result types that can be executed include the
following: ViewResult (which renders a view and is the most-often
used result type), RedirectToRouteResult, RedirectResult,ContentResult, JsonResult,
and EmptyResult.
|
Request Flow
ASP.NET
Web Forms
|
ASP.NET
MVC
|
Asp.Net
Web Form follow a traditional event driven development model.
|
Asp.Net
MVC is a lightweight and follow MVC (Model, View, Controller) pattern based
development model.
|
Asp.Net
Web Form has server controls.
|
Asp.Net
MVC has html helpers.
|
Asp.Net
Web Form supports view state for state management at client side.
|
Asp.Net
MVC does not support view state.
|
Asp.Net
Web Form has file-based URLs means file name exist in the URLs must have its
physically existence.
|
Asp.Net
MVC has route-based URLs means URLs are divided into controllers and actions and
moreover it is based on controller not on physical file.
|
Asp.Net
Web Form follows Web Forms Syntax
|
Asp.Net
MVC follow customizable syntax (Razor as default)
|
In
Asp.Net Web Form, Web Forms(ASPX) i.e. views are tightly coupled to Code
behind(ASPX.CS) i.e. logic.
|
In
Asp.Net MVC, Views and logic are kept separately.
|
Asp.Net
Web Form has Master Pages for consistent look and feels.
|
Asp.Net
MVC has Layouts for consistent look and feels.
|
Asp.Net
Web Form has User Controls for code re-usability.
|
Asp.Net
MVC has Partial Views for code re-usability.
|
Asp.Net
Web Form has built-in data controls and best for rapid development with
powerful data access.
|
Asp.Net
MVC is lightweight, provide full control over markup and support many
features that allow fast & agile development. Hence it is best for
developing interactive web application with latest web standards.
|
Asp.Net
Web Form is not Open Source.
|
Asp.Net
Web MVC is an Open Source.
|
ASP.NET MVC Features
¨ Runs
on top of ASP.NET
¤ Not
a replacement for WebForms
¤ Leverage
the benefits of ASP.NET
¨ Embrace
the web
¤ User/SEO
friendly URLs, HTML 5, SPA
¤ Adopt
REST concepts
¨ Uses
MVC pattern
¤ Conventions
and Guidance
¤ Separation
of concerns
¨ Tight
control over markup
¨ Testable
¨ Loosely
coupled and extensible
¨ Convention
over configuration
¨ Razor
view engine
¤ One
of the greatest view engines
¤ With
intellisense, integrated in Visual Studio
¨ Reuse
of current skills (C#, LINQ, HTML, etc.)
¨ Application-based
(not scripts like PHP)
Separation of
Concerns
¨ Each
component has one responsibility
¤ SRP
– Single Responsibility Principle
¤ DRY
– Don’t Repeat Yourself
¨ More
easily testable
¤ TDD
– Test-driven development
¨ Helps
with concurrent development
¤ Performing
tasks concurrently
n One
developer works on views
n Another
works on controllers
Extensible
¨ Replace
any component of the system
¤ Interface-based
architecture
¨ Almost
anything can be replaced or extended
¤ Model
binders (request data to CLR objects)
¤ Action/result
filters (e.g. OnActionExecuting)
¤ Custom
action result types
¤ View
engine (Razor, WebForms, NHaml, Spark)
¤ View
helpers (HTML, AJAX, URL, etc.)
¤ Custom
data providers (ADO.NET), etc.
Clean URL’s
¨ REST-like
¤ /products/update
¤ /blog/posts/2014/11/28/mvc-is-cool
¨ Friendlier
to humans
¤ /product.aspx?catId=123
or post.php?id=123
¤ Becomes
/products/chocolate/
¨ Friendlier
to web crawlers
¤ Search
engine optimization (SEO)
ASP.NET MVC Release
History
Date
|
Version
|
10 December 2007
|
ASP.NET MVC
|
13 March 2009
|
ASP.NET MVC 1.0
|
16 December 2009
|
ASP.NET MVC 2 RC
|
4 February 2010
|
ASP.NET MVC 2 RC
2
|
10 March 2010
|
ASP.NET MVC 2
|
6 October 2010
|
ASP.NET MVC 3
Beta
|
9 November 2010
|
ASP.NET MVC 3 RC
|
10 December 2010
|
ASP.NET MVC 3 RC
2
|
13 January 2011
|
ASP.NET MVC 3
|
20 September 2011
|
ASP.NET MVC 4
Developer Preview
|
15 February 2012
|
ASP.NET MVC 4
Beta
|
31 May 2012
|
ASP.NET MVC 4 RC
|
15 August 2012
|
ASP.NET MVC 4
|
30 May 2013
|
ASP.NET MVC 4
4.0.30506.0
|
26 June 2013
|
ASP.NET MVC 5
Preview
|
23 August 2013
|
ASP.NET MVC 5 RC
1
|
17 October 2013
|
ASP.NET MVC 5
|
17 January 2014
|
ASP.NET MVC 5.1
|
10 February 2014
|
ASP.NET MVC 5.1.1
|
4 April 2014
|
ASP.NET MVC 5.1.2
|
22 June 2014
|
ASP.NET MVC 5.1.3
|
1 July 2014
|
ASP.NET MVC 5.2.0
|
28 August 2014
|
ASP.NET MVC 5.2.2
|
What’s new in MVC 4?
¨ ASP.NET
Web API
¨ Refreshed
and modernized default project templates
¨ New mobile
project template
¨ Many
new features to support mobile apps
¨ Enhanced
support for asynchronous methods
What’s new in MVC 5?
What’s new in MVC 6?
Rebuilt from the Ground
Up
¨
MVC, Web API, and Web Pages are merged into one
framework, called MVC 6. The new framework uses a common set of abstractions
for routing, action selection, filters, model binding, and so on.
¨
Dependency injection is built into the
framework. Use your preferred IoC container to register dependencies.
¨
vNext is host agnostic. You can host your app in
IIS, or self-host in a custom process. (Web API 2 and SignalR 2 already support
self-hosting; vNext brings this same capability to MVC.)
¨
vNext is open source and cross platform.
Leaner, Faster
¨
MVC 6 has no dependency on System.Web.dll. The result
is a leaner framework, with faster startup time and lower memory consumption.
¨
vNext apps can use a cloud-optimized runtime and
subset of the .NET Framework. This subset of the framework is about 11
megabytes in size compared to 200 megabytes for the full framework, and is
composed of a collection of NuGet packages.
¨
Because the cloud-optimized framework is a
collection of NuGet packages, your app can include only the packages you
actually need. No unnecessary memory, disk space, loading time, etc.
¨
Microsoft can deliver updates to the framework
on a faster cadence, because each part can be updated independently.
True Side-by-Side Deployment
¨
The reduced footprint of the cloud-optimized
runtime makes it practical to deploy the framework with your app.
¨
You can run apps side-by-side with different
versions of the framework on the same server.
¨
Your apps are insulated from framework changes
on the server.
¨
You can make framework updates for each app on
its own schedule.
¨
No errors when you deploy to production resulting
from a mismatch between the framework patch level on the development machine
and the production server.
New Development Experience
¨
vNext uses the Roslyn
compiler to compile code dynamically.
¨
You can edit a code file, refresh the browser,
and see the changes without rebuilding the project.
¨
Besides streamlining the development process,
dynamic code compilation enables development scenarios that were not possible
before, such as editing code on the server using Visual Studio Online (“Monaco”).
¨
You can choose your own editors and tools.